Ligand Binding to a Receptor Kinase Results in
All of these answer options are correct. Trk receptor transactivation was necessary for activation of Akt and extracellular.

Schematic Representation Of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase And Downstream Download Scientific Diagram
In the canonical model of HER receptor activation ligand binding to the ECDs results in receptor dimerization by promoting an extended conformation of the ECD 16 17 18 19.
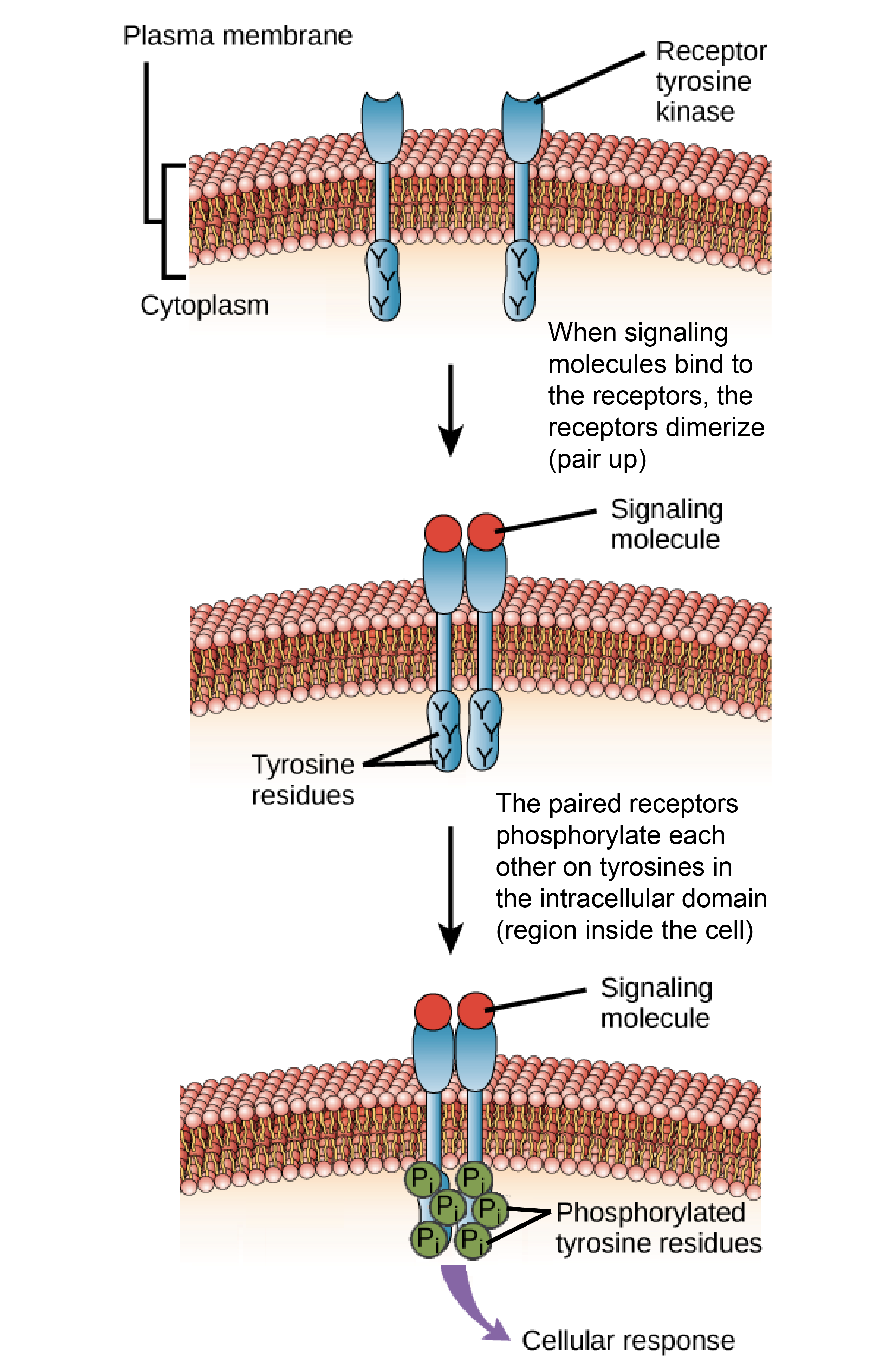
. Binding of cytoplasmic signaling molecules. Ligand-induced oligo-merization required tyrosine kinase activity and nine different tyrosine kinase substrate residues. All of these choices are correct.
Photoaffinity labeling is the only biochemical technique for detecting direct ligand. Ligand binding to G-protein coupled receptors results in conversion of RhoA-GTP to RhoA-GDP. Effect of ligand on LYP18 and 4F8 binding PRP diluted to 1 107 plate- Ligand-induced changes in receptor conformation termed Ligand- letsml with PBS or HEK-293 cells transfected with wild type GPIIbIIIa Induced Binding Sites LIBS 8 9 may also play a role in outside-in 3 106 cellsml in HBBS or mock transfected cells.
This indicates that the binding of signaling molecules to activated EGFRs results in. How does this mutation influence RAS activity. ABinding of the ligand activates a G-protein close to the receptor tyrosine kinase.
It reassembles with the β beta and γ gamma subunits. Confirming whether CLV2 and RPK2 directly bind the CLV3 peptide is essential for understanding the mechanism of stem cell mainte-nance in the SAM. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors EGFR ErbB1 HER1 This RTK subclass is activated by epidermal growth factor resulting in cell division that leads to cell growth proliferation and differentiation.
Signaling by transmembrane receptor kinases which are composed of an extracellular ligand-binding domain a single transmembrane helix and an intracellular kinase domain is fundamental to. View Test Prep - CHAPTER 9 from BIOLOGY 2107 at Georgia State University. The ligand-binding domain provides a negative constraint on tyrosine kinase activity and.
BBinding of the signal causes receptors to form a dimer. Binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator or α 2-macroglobulin α 2 M to LRP1 resulted in Src family kinase SFK activation and SFK-dependent Trk receptor transactivation in PC12 cells and neurons. It no longer activates an effector protein.
Binding of cytoplasmic signaling molecules. Growth factors occur in both monomeric eg EGF TGF-a and dimeric eg PDGF CSF-i NGF forms. Ligand binding to the extracellular domain results in receptor dimerization.
Phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor. DBinding of the ligand results in the phosphorylation of tyrosines. CK and BR bind to the CRE1 receptor and the BRI1 receptor respectively and ligand binding activates the kinase domain and induces protein phosphorylation.
Here we identified a member of the Elicitor Peptide PEP family namely PEP7 as the specific ligand of receptor kinase SIRK1. BR promotes the interaction between BRI1 and its co-receptor BAK1 and this interaction is required for activation of the kinase domain in BRI1. These events include receptor dimerization activation of intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. Increased kinase activity through autophosphorylation. In PC12 cells and neurons binding of two structurally distinct ligands to LRP1 activated Src family kinases which then activated Trk receptors as measured by Trk receptor tyrosine phosphorylation the activity of two downstream kinases Akt and extracellular signalregulated kinase 1 and 2 and neurite outgrowth assays.
CBinding of the ligand activates a tyrosine kinase in the cytoplasm. How does ligand binding to a receptor tyrosine kinase result in the activation of RAS. The widely different chemical nature of these agents suggests that they do not act by direct interaction with specific allosteric regulatory sites but rather by facilitating the interactions between kinase molecules.
The two adjacent tyrosine kinase domains phosphorylate one another to tyrosine residues autophosphorylation. Phosphorylation of tyrosines on the C-terminal tail of the EGF receptor 4 5 6 generates binding sites for the Src homology 2 SH2 and PTB domain-containing proteins that mediate the downstream effects. Cell-surface receptors are membrane-anchored proteins that bind to ligands on the outside surface of the cell.
Through a still unclear mechanism the ECD dimer communicates with the intracellular fragments of the receptor. RhoA-GTP dissociates from RhoA-GDPi allowing RhoA to bind downstream. Ligand binding to a receptor kinase results in.
The signal of ligand binding is transduced through the structure of the receptor and results in the activation of the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. As signaling proceeds activated receptors will bind to phosphotyrosine-binding proteins such as actin Cbl and Grb2 resulting in the oligomerization of the EGFR. What mutation is commonly found in RAS genes in cancer cells.
PEP7 binds to the extracellular domain of SIRK1 with a binding constant of 144 079 µM and is secreted to the apoplasm specifically in response to sucrose treatment. Here we describe a signaling pathway whereby LRP1 transactivates Trk receptors. Who are the experts.
Phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor. These results support the hypothesis that full-length receptor aggregation itself induced by ligand binding to the extracellular domain results in intracellular. Given that ligand binding is essential for the rapid internalization of epidermal growth factor receptor EGFR the events induced by ligand binding probably contribute to the regulation of EGFR internalization.
Receptors because the binding of ligands to their recep-tors is the initial reaction that occurs in secreted ligand-dependent cellcell communication. Ligand binding to a receptor kinase results in. Ligand binding induced the formation of receptor oligomers which were found in both the plasma membrane and intracellular structures.
CHAPTER 9 1Ligand binding to a receptor kinase results in. So many different kinds of molecules including large hydrophilic or water-loving ones may act as ligands. In this type of signaling the ligand does not need to cross the plasma membrane.
RECOGNITION AND BINDING OF LIGAND The first step in the activation of growth factor receptors is the binding of ligand to its cognate receptor. Stabilization of a signaling complex involving. Ligand binding induces a conformational change in the ectodomain leading to the reorientation of the intracellular kinase domains resulting in the activation of the asymmetric kinase dimer.
RTKs bind growth factors to signal processes that result in the regulation of cell growth differentiation and survival through gene transcription.

Upon Ligand Binding Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Rtks Dimerize And Download Scientific Diagram

Upon Ligand Binding Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Rtks Dimerize And Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment